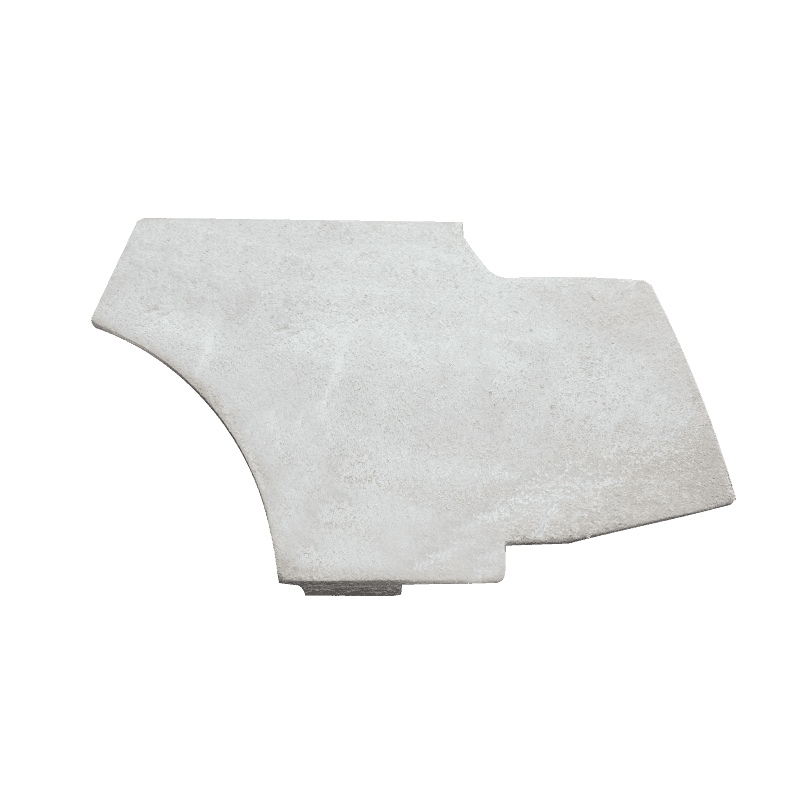
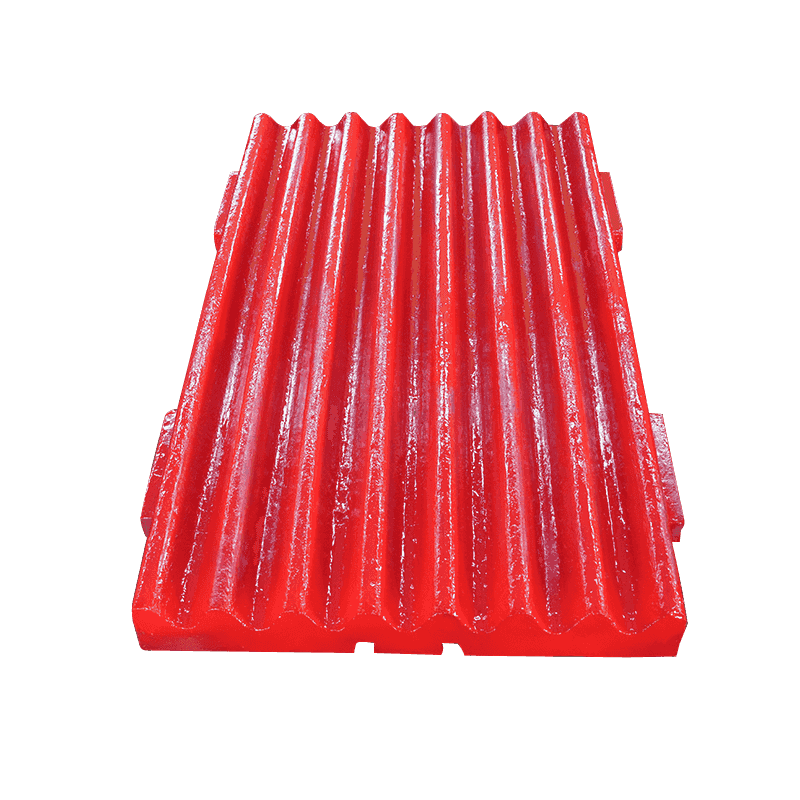
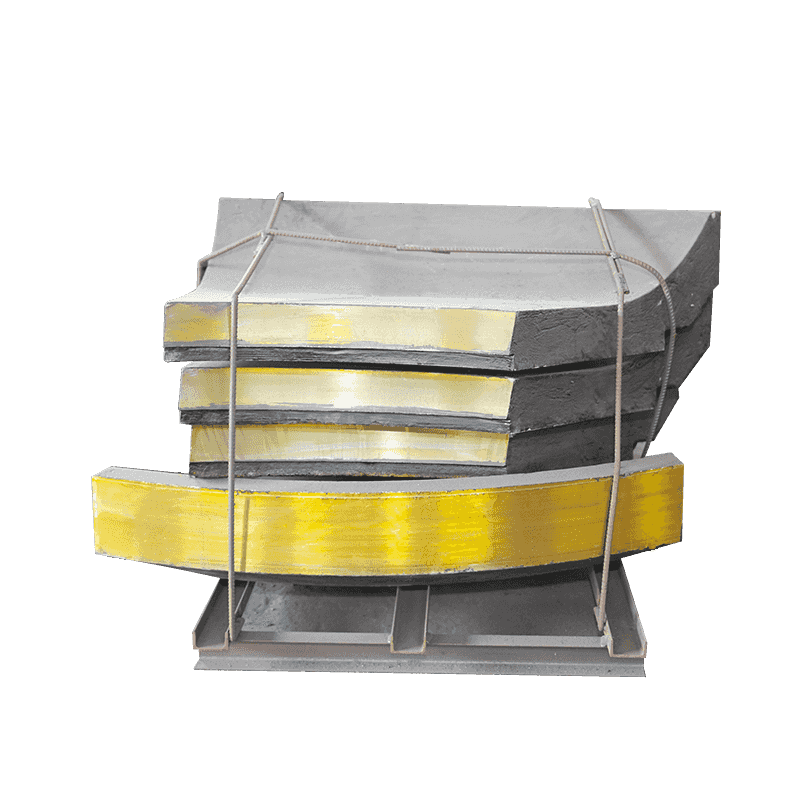
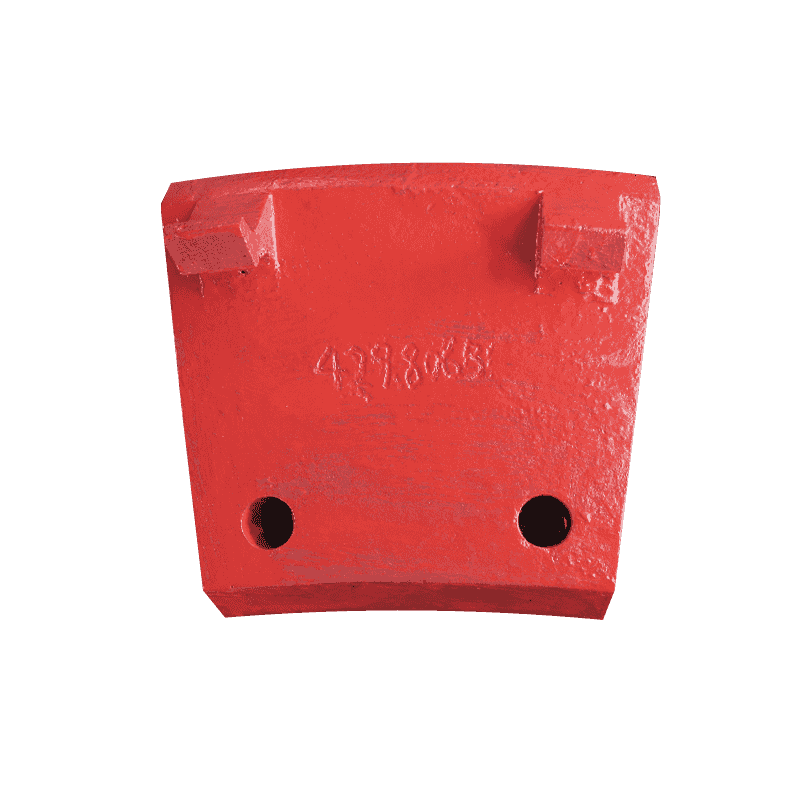
How Does Advanced High Manganese Steel Maximize Jaw Crusher Protection and Durability?
In the highly demanding field of material reduction, the operational longevity and efficiency of heavy machinery like jaw crushers hinge entirely on the performance of their critical wear parts. Among these components, the side guard plate plays a defensive role, acting as the primary shield protecting the main crusher body. The latest advancements in metallurgical science have led to the development of side guard plates forged from high manganese steel alloys, specifically designed to withstand the incessant, high-intensity impact and abrasion inherent to crushing cycles. This feature delves into the precision engineering and material composition that establish these plates as the standard for maintaining structural integrity and operational uptime in crushing operations.
The Foundation of Resilience: High Manganese Steel Alloy Composition
The core strength of the side guard plate lies in its meticulously crafted high manganese steel alloy. The precise metallurgical formula ensures a dynamic balance between exceptional toughness—the resistance to fracture—and superior hardness, which dictates wear resistance.
The composition centers around a significant percentage of manganese (Mn), typically ranging from 11% to 14%. This concentration is the catalyst for the steel’s signature characteristic: its ability to work-harden under impact. When subjected to the severe pressures and repeated blows of crushing materials, the steel’s surface rapidly hardens while the subsurface layers retain their initial ductility and toughness. This unique mechanism creates a highly protective, impact-resistant shield that constantly renews its wear surface during operation.
Complementing the manganese, the alloy includes 0.9% to 1.5% silicon (Si), which acts primarily as a deoxidizer during the casting process, ensuring the purity and soundness of the final Jaw Crusher High Manganese Steel Castings. Furthermore, chromium (Cr), typically present between 0.4% and 1.0%, contributes significantly to the formation of hard carbides within the steel structure. These carbides further boost the initial hardness and abrasive wear resistance, especially before work-hardening fully takes effect. Trace elements such as phosphorus (P), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), and molybdenum (Mo) are also included, each playing a subtle yet critical role in refining the grain structure and enhancing the overall mechanical properties of the casting, guaranteeing consistent and high-quality performance.
Engineered Geometry: Strategic Protection Against Impact
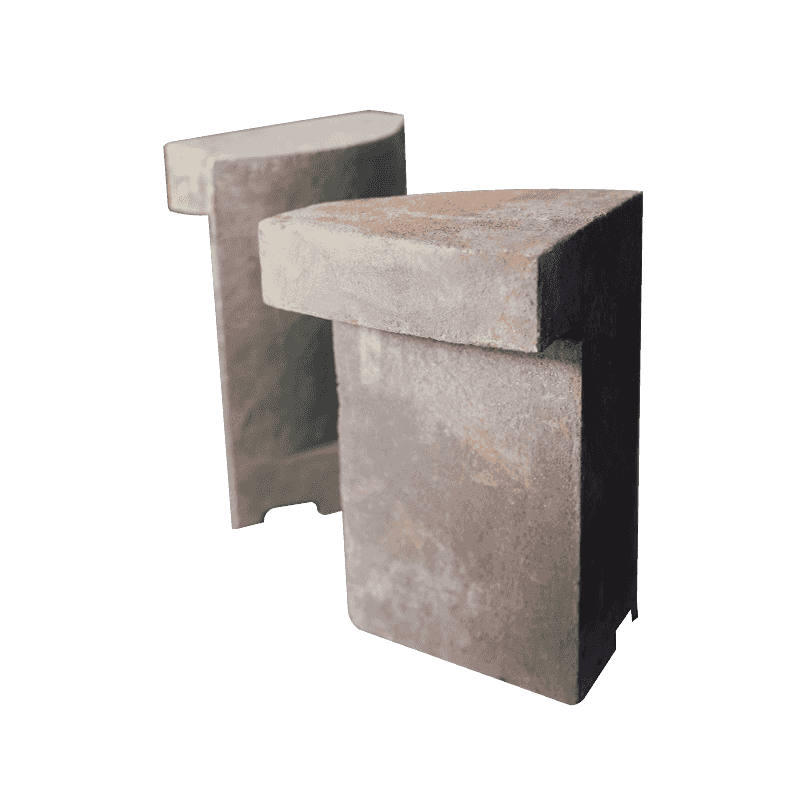
The functional design of the side guard plate is a testament to focused engineering, where geometry is optimized specifically for defense against material impact. The plate’s main function is to prevent direct contact between the abrasive feed material and the expensive, non-replaceable body or frame of the jaw crusher.
Designers typically incorporate a substantially thicker structure into the side guard plate compared to other components in the crushing chamber. This increased thickness is a direct measure to enhance impact absorption capacity. The sheer mass of the plate allows it to absorb and dissipate the kinetic energy transferred by high-velocity material fragments thrown laterally within the crushing chamber. Without this critical buffer, the constant bombardment would quickly erode the main steel frame, leading to premature structural failure and costly downtime.
Moreover, the edges and designated contact areas of the side guard plate often feature a reinforced design. These areas—where material tends to jam or where impact angles are most acute—are structurally optimized to withstand the highest intensity of wear and abrasion. This reinforcement ensures that the defensive integrity is maintained even in the most stressed zones, maximizing the life cycle of the guard plate itself and securing continuous protection for the crusher body. The casting process, which produces these specialized Jaw Crusher High Manganese Steel Castings, allows for the creation of these complex, reinforced geometries with high precision.
Dual-Action Enhancement: Corrosion Resistance in Complex Environments
A critical and often overlooked requirement for crushing components is resistance to environmental degradation. Crushing operations frequently involve materials that are wet, clay-heavy, or contain mildly corrosive elements. This environment poses a significant threat to ordinary steel, as abrasion breaks down the protective surface oxide layer, exposing the underlying metal to rust and chemical attack.
This is where the inclusion of chromium and silicon in the high manganese alloy becomes paramount. Chromium is renowned for its role in forming a passive, self-repairing oxide layer on the steel surface, dramatically improving the material’s inherent corrosion resistance. This characteristic ensures that the side guard plate maintains good performance in complex, moist, or potentially corrosive crushing environments.
Similarly, silicon not only contributes to the strength of the casting but also plays a role in enhancing oxidation resistance at slightly elevated temperatures and contributes to the overall stability of the protective surface film. The combined effect of chromium and silicon means that the Jaw Crusher High Manganese Steel Castings used for these side guards resist both mechanical wear (abrasion) and chemical wear (corrosion) simultaneously, offering a truly robust protective solution.
Operational Longevity and Economic Defense
The primary benefit delivered by the high-performance side guard plate is its role in enabling extended, continuous operation of the jaw crusher. By effectively sacrificing itself to protect the main frame, the plate ensures that the expensive, fundamental structural elements of the crusher remain undamaged.
The use of an alloy with a precise ratio of manganese, silicon, and chromium delivers predictable wear rates, allowing maintenance schedules to be planned with accuracy. The ability of the Jaw Crusher High Manganese Steel Castings to work-harden means that the wear-life is maximized, reducing the frequency of component changeouts. This combination of advanced material science and defensive engineering ensures maximum operational efficiency and provides an unyielding shield against the relentless forces of material reduction. This focus on maximizing the protection of core machinery confirms the side guard plate's status as a strategically engineered, mission-critical component.

 English
English  русский
русский  عربى
عربى