Does Precise Alloy Engineering Hold the Key to Unrivaled Jaw Crusher Durability?
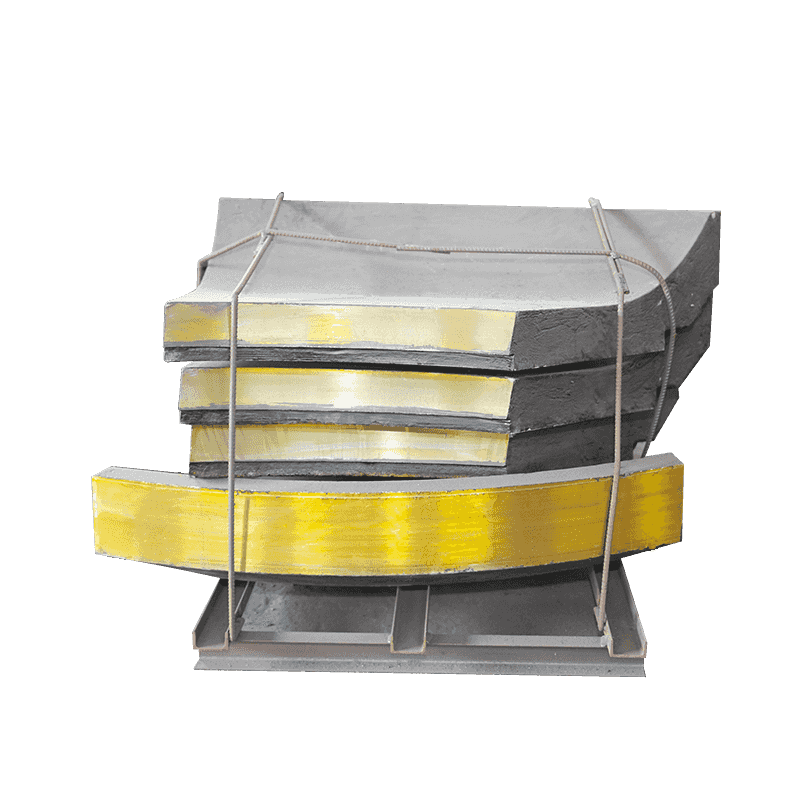
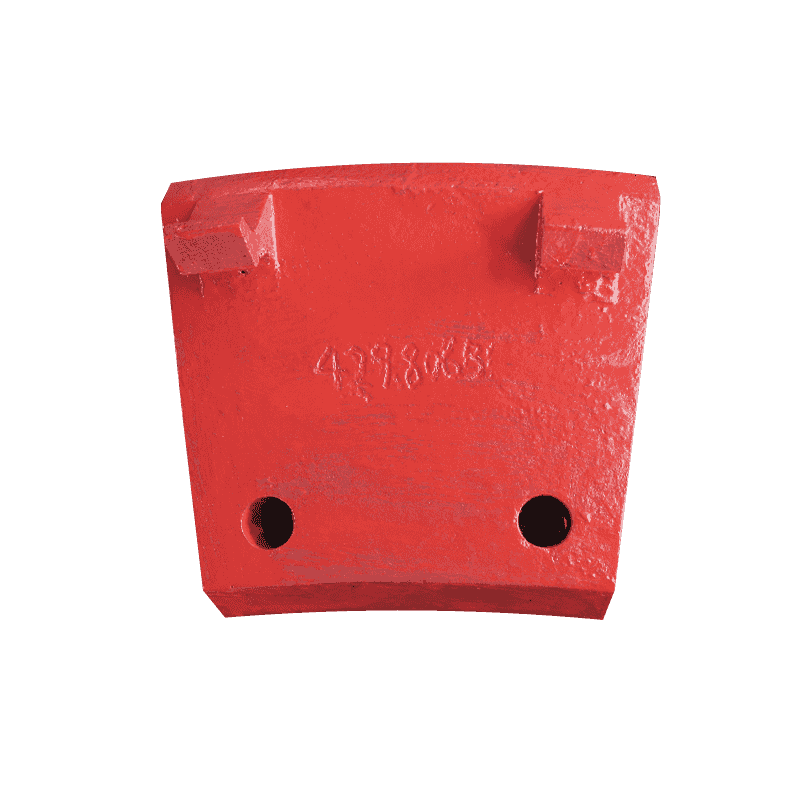
A detailed technical analysis confirms the exceptional properties of a newly specified High Manganese Steel Castings side guard, often referred to as a jaw crusher wear plate, designed for rigorous duty in primary jaw crushing equipment. This critical component, engineered specifically to withstand extreme impact and abrasive wear, represents a crucial advancement in maximizing the operational life and integrity of the crusher structure. The focus of this technical document is the fusion of advanced metallurgy with optimized structural design for superior high Mn steel wear resistance.
The Foundation of Resilience: High Manganese Steel Castings
The side guard plate is fabricated from a proprietary high manganese steel alloy, a material chosen for its unique work-hardening characteristics, making it an ideal manganese steel crusher liner. The component’s performance is intrinsically linked to its carefully controlled chemical composition, which dictates its resultant mechanical properties—specifically, its remarkable ability to achieve high hardness and superior toughness simultaneously under operational stress.
The core of this material's strength lies in its manganese content, which is maintained at a high level. At the specified concentration of 11–14% Manganese (Mn), the steel adopts an austenitic structure. This structure is inherently stable but prone to transformative hardening when subjected to impact. During crushing operations, the material’s surface immediately work-hardens upon impact, increasing the surface hardness to levels far exceeding its initial condition. This mechanism creates a durable, impact-resistant outer layer that resists abrasive wear, while the underlying core remains tough and ductile, preventing catastrophic failure from cracking or fracture. The use of this Hadfield steel variation is paramount for longevity.
Synergistic Alloying Elements
Beyond manganese, the precise incorporation of auxiliary elements ensures a well-rounded performance profile capable of handling complex operational environments. This specialized austenitic steel jaw crusher part benefits from these additions.
Silicon (Si): Present at 0.9–15%, silicon acts as a powerful deoxidizer during the casting process, enhancing the cleanliness of the molten alloy and preventing the formation of detrimental inclusions. Crucially, silicon also contributes to the material's overall strength and elasticity. This percentage range is meticulously controlled to ensure optimum fluidity for complex casting geometries while maintaining the necessary mechanical properties for impact resistance, a key factor for any heavy-duty crusher component.
Chromium (Cr): The inclusion of 0.4–1.0% Chromium (Cr) is a strategic addition specifically targeting abrasive wear and corrosion. Chromium forms hard carbides that are distributed throughout the microstructure, providing fixed points of high hardness that resist abrasion from rock and aggregate movement. Furthermore, chromium significantly improves the corrosion resistance of the high manganese steel. This is essential for crushers processing wet materials, acidic ores, or aggregates containing high moisture, ensuring the impact crusher side guard alloy maintains its structural integrity and performance profile even in chemically challenging conditions.
Trace Elements for Stability and Integrity: Trace amounts of phosphorus (P), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), and molybdenum (Mo) are managed within the alloy. These elements play roles in refining the grain structure, enhancing homogeneity, and further optimizing the mechanical response of the casting. Nickel and molybdenum, even in trace amounts, contribute subtly but effectively to improved toughness and fracture resistance, particularly at varied operating temperatures.
Composition Breakdown
The following table summarizes the key alloy components and their primary contributions to the side guard's performance:
|
Component |
Percentage Range (Wt. %) |
Primary Function in Alloy |
|---|---|---|
|
Manganese (Mn) |
11.0 – 14.0 |
Austenitic structure, work-hardening, toughness |
|
Silicon (Si) |
0.9 – 15.0 |
Deoxidizer, strength, casting fluidity |
|
Chromium (Cr) |
0.4 – 1.0 |
Abrasive wear resistance, corrosion resistance |
|
Trace Elements |
P, Ni, Cu, Mo (Minor) |
Grain refinement, toughness optimization |
Engineered for Protection: Structural Design and Function
The design of the crusher body protection plate is a direct response to its primary functional mandate: to shield the main body of the jaw crusher from damage inflicted by the constant, high-energy impact of material being processed. The geometry and thickness are not arbitrary; they are the result of comprehensive engineering optimization.
Designers universally adopt a thicker structural profile for this component. This increased mass is critical for two reasons:
Kinetic Energy Absorption: A greater cross-section provides a larger buffer for absorbing and dissipating the immense kinetic energy transmitted by impacting material, minimizing the transfer of shock loads to the main crusher frame. This maximizes jaw crusher liner lifespan.
Wear Volume: Increased thickness means a greater volume of sacrificial material is available. Since wear is inevitable, designing for longevity involves maximizing the amount of material that can be removed before the component needs replacement, thereby extending service intervals and reducing maintenance frequency. This is crucial for reducing crusher component downtime.
In addition to the overall thickness, the side guard design incorporates reinforced edges and contact areas. These are the zones that experience the most acute forms of concentrated wear and impact during the crushing cycle. By strategically thickening and profiling these critical areas, the design ensures localized stress concentrations are managed effectively, maintaining the component’s integrity under sustained, heavy-duty operation.
The combination of the work-hardening High Manganese Steel Castings and the reinforced structural geometry creates a component that dynamically protects the crushing chamber. As material is fed and compressed, the side guard directs the flow, prevents 'cheeking' or excessive friction against the frame, and acts as the ultimate sacrificial barrier. The ability of the alloy’s surface to rapidly harden ensures that even when dealing with extremely hard aggregates, the wear rate is minimized. This makes it a superior Manganese steel side liner.
Maintaining Performance in Complex Environments
A significant design consideration is the operational environment. Crushers frequently operate in conditions involving high moisture, slurry, or chemically active materials. The 0.4–1.0% Chromium content is crucial here. While high manganese steels are generally known for their wear properties, the chromium addition elevates the side guard's resistance to environmental degradation, a key factor often overlooked. This improved corrosion resistance ensures that surface pitting or chemical degradation does not compromise the mechanical stability of the plate over time. The jaw crusher side guard is designed not just to resist impact, but to maintain its protective role consistently, regardless of whether the material being crushed is wet, dry, abrasive, or mildly corrosive.

 English
English  русский
русский  عربى
عربى